webrtc developers
The WebRTC APIs
Three main tasks
- Acquiring audio and video
- Communicating audio and video
- Communicating arbitrary data
Three main JavaScript APIs
- MediaStream(aka getUserMedia)
- RTCPeerConnection
- RTCDataChannel
MediaStream
(Acquiring audio and video)
MediaStream
- Pepresent a stream of audio and/or video
- Can contain multiple ‘tracks’
- Obtain a MediaStream with navigator.getUserMedia()
Constraints
- Controls the contents of the MediaStream
- Media type, resolution, frame rate
RTCPeerConnection
(Audio and video communication between peers)RTCPeerConnection does a lot
- Signal processing
- Codec handling
- Peer to peer communication
- Security
- Bandwidth management
WebRTC architecture
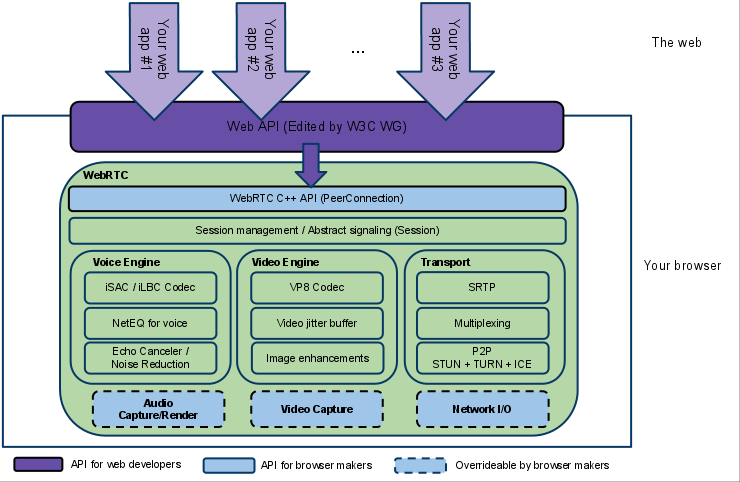
RTCDataChannel
(Bidirectional communication of arbitrary data between peers)
RTCDataChannel
- Same API as WebSockets
- Ultra-low latency
- Unreliable or reliable
- Secure
Servers and Protocols
(Peer to peer — but we need servers :)
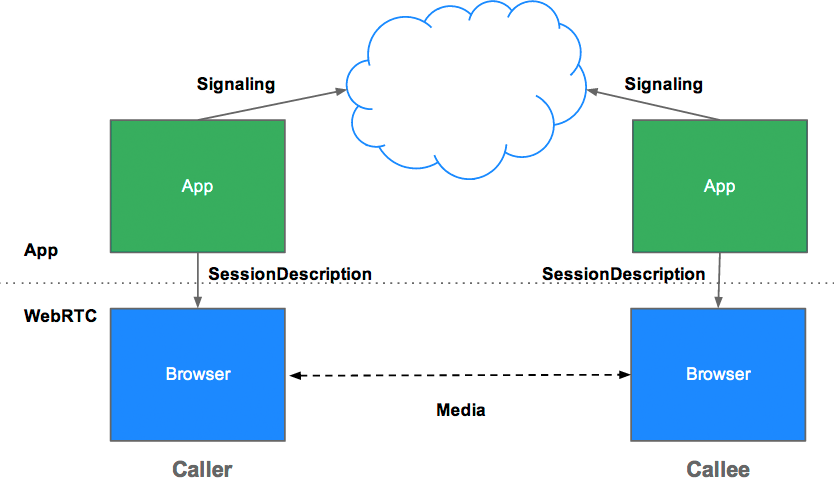
Abstract Signaling
- Need to exchange ‘session description’ objects:
- What formats I support, what I want to send
- Network information for peer-to-peer setup
- Can use any messaging mechanism
- Can use any messaging protocol
STUN and TRUN
(P2P in the age of firewalls and NATs)
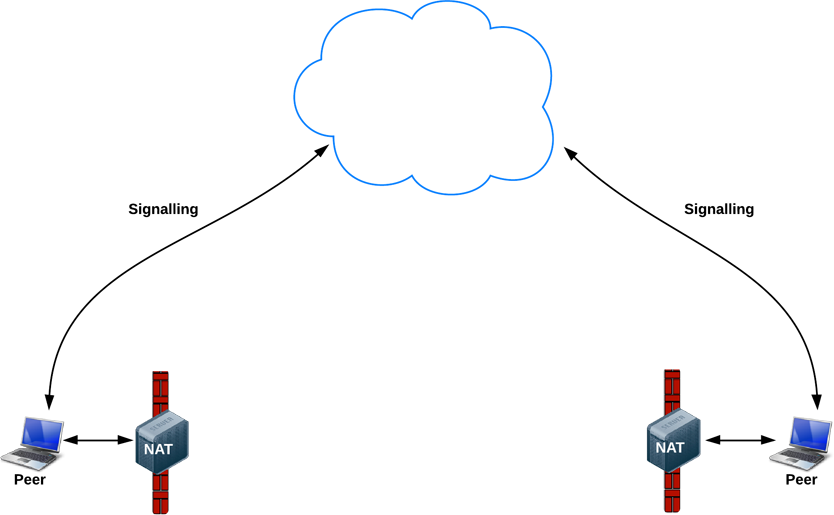
An ideal world
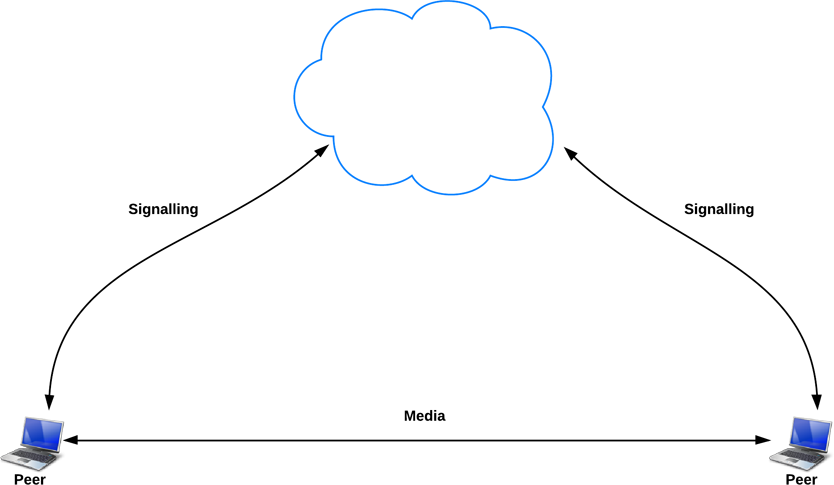

The real world
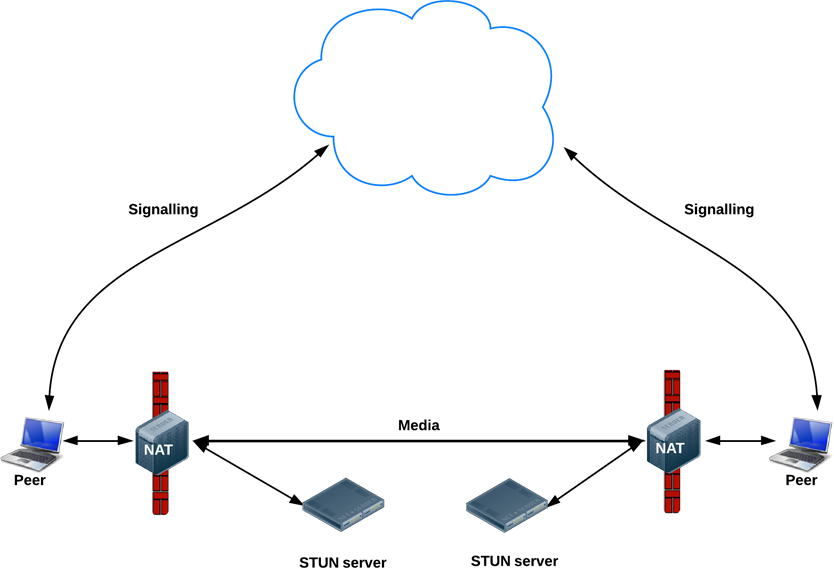
STUN
- Tell me what my public IP address is
- Simple server, cheap to run
- Data flows peer-to-peer
TURN
- Provide a cloud fallback if peer-to-peer communication fails
- Data is sent through server, uses server bandwidth
- Ensures the call works in almost all environments
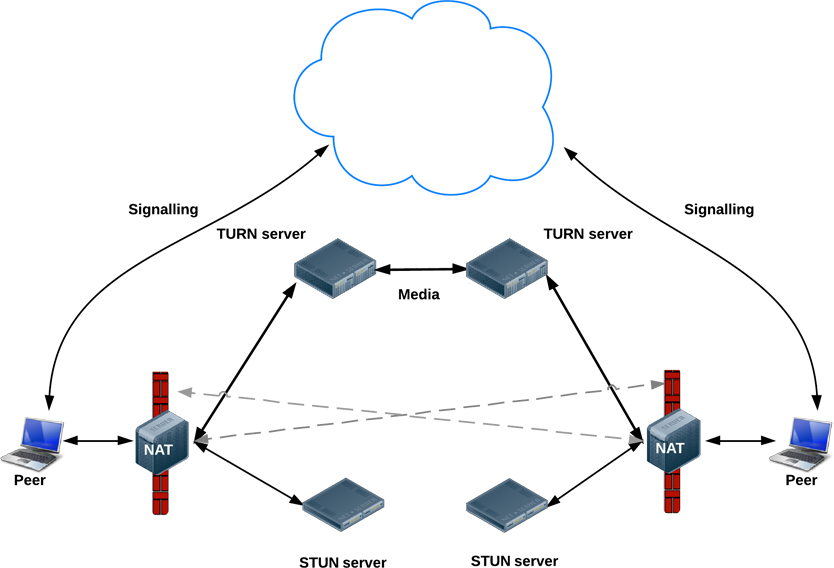
ICE
- ICE: a framework for connecting peers
- Tries to find the best path for each call
- Vast majority of calls can use STUN (webrtcstats.com):
Deploying STUN/TURN
- stun.l.google.com:19302
- WebRTC stunserver, turnserver
- rfc5766-turn-server
- restund
Security
Security throughout WebRTC
- Mandatory encryption for media and data
- Secure UI, explicit opt-in
- Sandboxed, no plugins
- WebRTC Security Architecture
Architectures
Peer to Peer : one-to-one call
clientA <——–> clientB
Mesh: small N-way call
1 | clientA <-------------> clientB |
Star: medium N-way call
1 | clientA <---------> clientB |
MCU: large N-way call
1 | MCU <-------------->clientA |

